Director/a de orquesta.
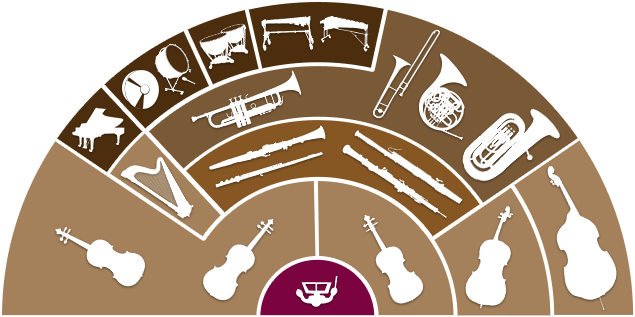
Cuerda frotada. De izquierda a derecha: violiones I, violines II, violas, violonchelos y contrabajos.
Viento madera: flautas, clarinetes, oboes, fagot y contrafagot.
Viento metal: trompetas, trompas, trombones y tubas.
Familia de percusión: percusión determinada (marimba, vibráfono, timbales, etc.) e indeterminada (platos, caja, gong, etc.)
El arpa y el piano, cuando no son solistas, no siempre están presentes en todas las obras para orquesta. Cuando son necesarios se sitúan en ese lugar.
There are different ways to classify musical instruments. One way is to group them as they are in a Western orchestra: strings, wind (woodwind and brass), and percussion.
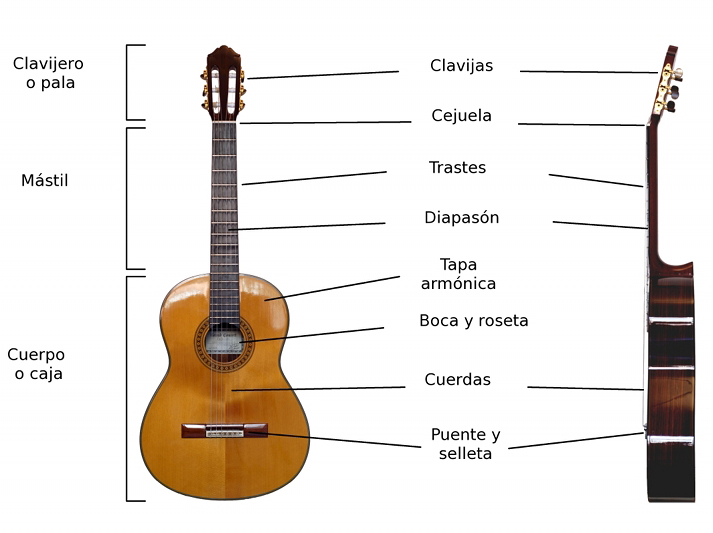
INSTRUMENT FAMILIES
BOWED STRING INSTRUMENTS
.
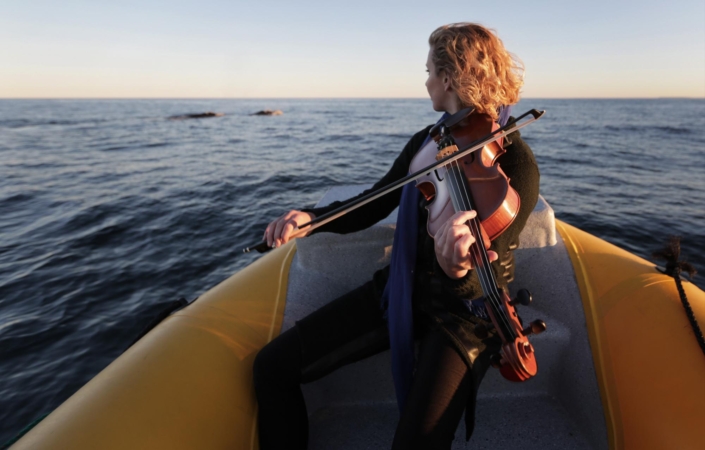
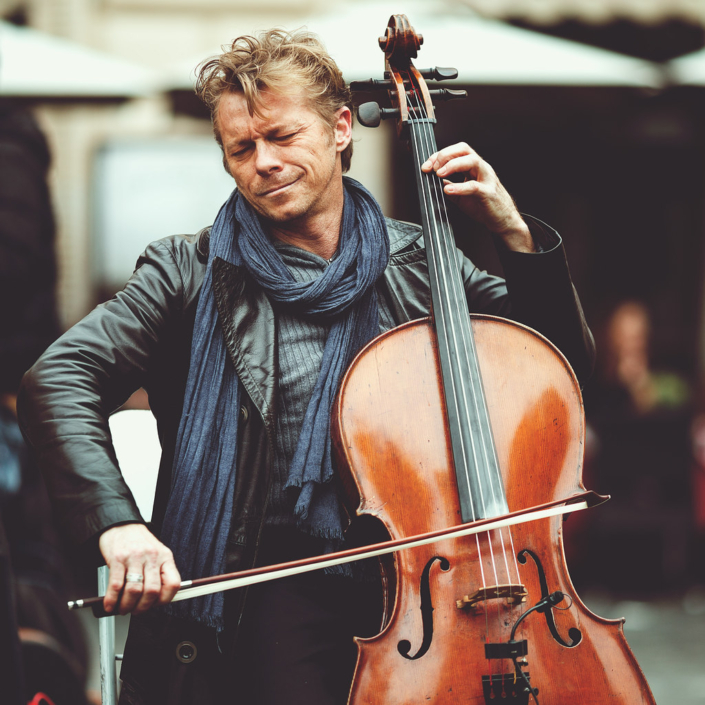
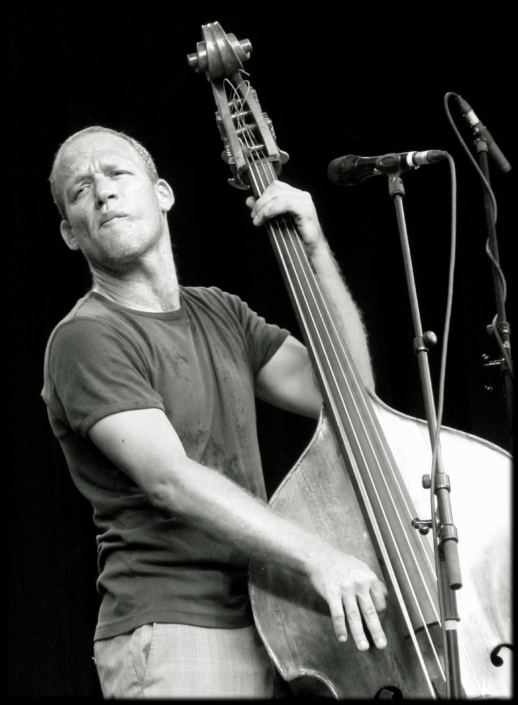
Bowing is a method used in some string instruments, including the violin, viola, cello, and the double bass. The bow is a stick with many hairs stretched between its ends that make the strings vibrate.
.
.
.
.
PLUCKED STRING INSTRUMENTS
Plucking is the method of playing by using a finger or some type of plectrum on instruments such as the guitar, harp or lute. This category includes keyboard instruments such as the harpsichord, which uses feathers (now plastic plectra) to pluck the strings.
.
Teorba: B. Ferrari, Amanti, io vi so dire
.
.
Guitarra: Joaquín Rodrigo, Concierto de Aranjuez
.
Arpa: Sacred Dance, Claude Debussy
.
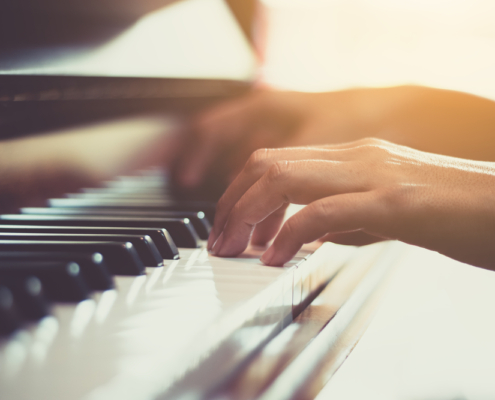
STRUCK STRING INSTRUMENTS
The third most common method of sound production in stringed instruments is to strike the string with a hammer. The most well-known instrument to use this method is the piano.
All pianos have two pedals. The soft pedal (the left one) changes the trajectory of the hammers so that they hit the strings softer. The damper pedal (the right one) raises all the dampers so that the strings can continue to vibrate when the keys have been released.
.
.
Lang Lang and Marquese ‘Nonstop’ Scott – Ocean 12¡¡
.
Javier Perianes, Chopin, Berceuse, Op. 57
.
Concierto para piano y orquesta nº 5 (Beethoven) – Daniel Baremboim
.
What Makes You Beautiful (Piano Guys Version)
WIND FAMILY
In wind instruments, sound is produced by the vibration of the air column inside the tube of the instrument. The pitch of sound is determined by the length of the air column and the thickness of the tubes. The longer and thicker a tube is, the lower the sound is. The shorter and thinner a tube is, the higher the sound is. Most wind instruments have different mechanisms (holes, keys, pistons, etc.) which change the length of the tubes and, therefore, their tuning.
Within the wind family, we distinguish between woodwind instruments and brass instruments.
WOODWIND INSTRUMENTS
A woodwind instrument produces sound when the player blows air against an edge or a thin piece of wood called a reed. Most of these instruments were originally made of wood, but some, such as the saxophone and some flutes, are now commonly made of other materials like metals or plastics.
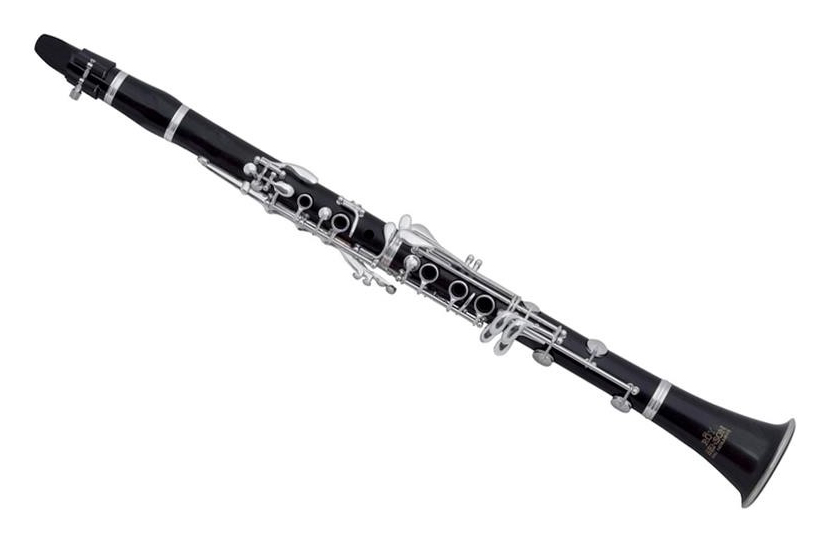
Single-reed instruments
.
A single-reed instrument uses just one reed. When air is forced between the reed and the mouthpiece, the reed vibrates, creating the sound. Single reed instruments include the clarinet and saxophone families.
.
.
.
.
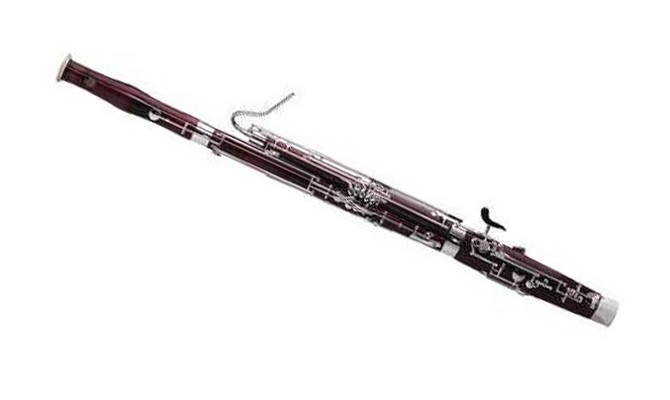
Double-reed instruments
.
A double-reed instrument uses two small pieces of cane joined together at the base. The air vibrates between the two pieces of cane. Double-reed instruments include the oboe, the cor anglais and the bassoon.
.
.
.
.
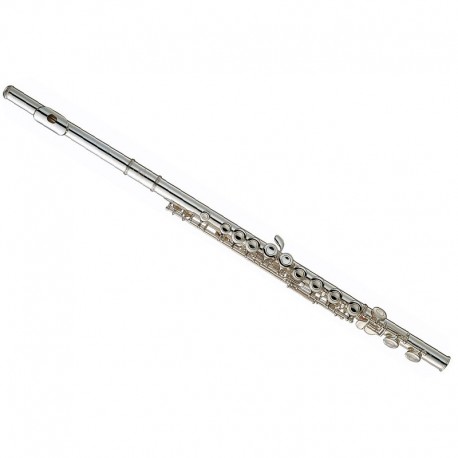
Edge
.
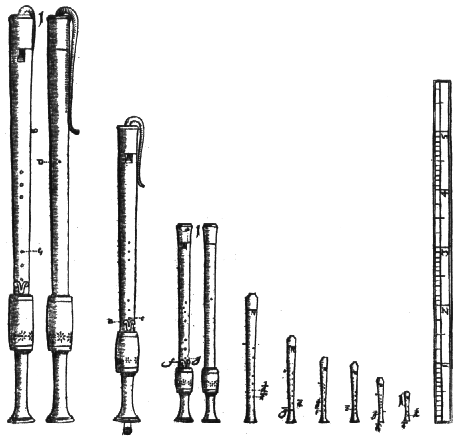
Flutes produce sound when air is blown across an edge. Flutes include transverse flutes and the recorder family.
.
.
.
.
John Dowland (1563-1626): The Earle of Essex Galiard
.
BRASS INSTRUMENTS
Mouthpiece
Pistons
A brass instrument produces different tones by the vibration of the player’s lips into an “embouchure”. Modern brass instruments generally come in one of two families: valved brass instruments which use a set of valves to change the pitch and slide brass instruments which use a slide to change the length of tubing. The main brass instruments are the french horn, the trumpet, the trombone and the tuba.
.
.
.
.
.
And more…
.
.
PERCUSSION INSTRUMENTS
A percussion instrument is any object which produces a sound by being hit with an drumstick, shaken or any other action which makes the object vibrate.
It is useful to note if a percussion instrument makes a definite pitch or indefinite pitch. For example, some percussion instruments (such as the marimba and timpani) can produce pitched notes and, therefore, can perform melodies. Other instruments (such as drum and crash cymbal) produce unpitched sounds and, therefore, can only perform rhythms, not melodies. Some of the main percussion instruments are the snare drum, the timpani, the xylophone, the vibraphone, the marimba and the triangle.
.
.
.
.
.
.
These are all the instruments that use electricity to produce sounds. There are two main types:
Electromechanic instruments are conventional instruments that incorporate a pickup or a contact microphone to amplify and modify the sound. The most popular example is the electric guitar.
Electronic instruments produce sound using oscillators which generate alternating currents. They also incorporate different electronic devices in order to modify sound parameters, achieving a wide variety of timbres, registers, and effects. The most common instruments are the synthesizer, the drum machine and the electronic drum.
.
Guitarra eléctrica (AC/DC – Highway to Hell).
.
.
Theremin y piano (La lista de Schindler)
.
.
INSTRUMENTAL ENSEMBLES
Just like voices, instruments can be played alone or in groups of different sizes.
Small groups that don’t usually have more than ten performers are called chamber groups. These are small groups of soloists in which each part of the composition is performed by a single player..
.
.
.
.
Quinteto (cuarteto de cuerda y piano).
.
.
The orchestra
In relation to big groups, the most important one is the orchestra. An orchestra is an instrumental ensemble, usually with string, brass, and woodwind sections, and possibly a percussion section as well. A smaller orchestra (of about fifty musicians or fewer) is called a chamber orchestra. A full size orchestra (about 100 musicians) may sometimes be called a symphony orchestra.
Conducting is the act of directing a musical performance by using visible gestures. Orchestras, choirs, concert bands and other musical ensembles often have conductors.
.
.
FSO 2016 Oficial | Harry Potter and the Philosopher’s Stone
.
Gustavo Dudamel – Bernstein: West Side Story – Mambo – Sinfónica Simón Bolívar Orchestra
.
Manfred Honeck & María Dueñas: Max Bruch und Antonín Dvořák
.